Your cart is currently empty!
How Long Will a Dog Bleed After Mating? Expert Insights
Published:
Updated:
Author:

If you’re a dog owner, you may have wondered about the reproductive cycle and what to expect after your female dog mates. There is often confusion surrounding the post-mating period, specifically regarding how long a dog will bleed after mating. This article aims to provide a clear and concise answer to this common question, ensuring you have the necessary knowledge to best care for your furry friend in this delicate period.
Understanding Canine Reproduction
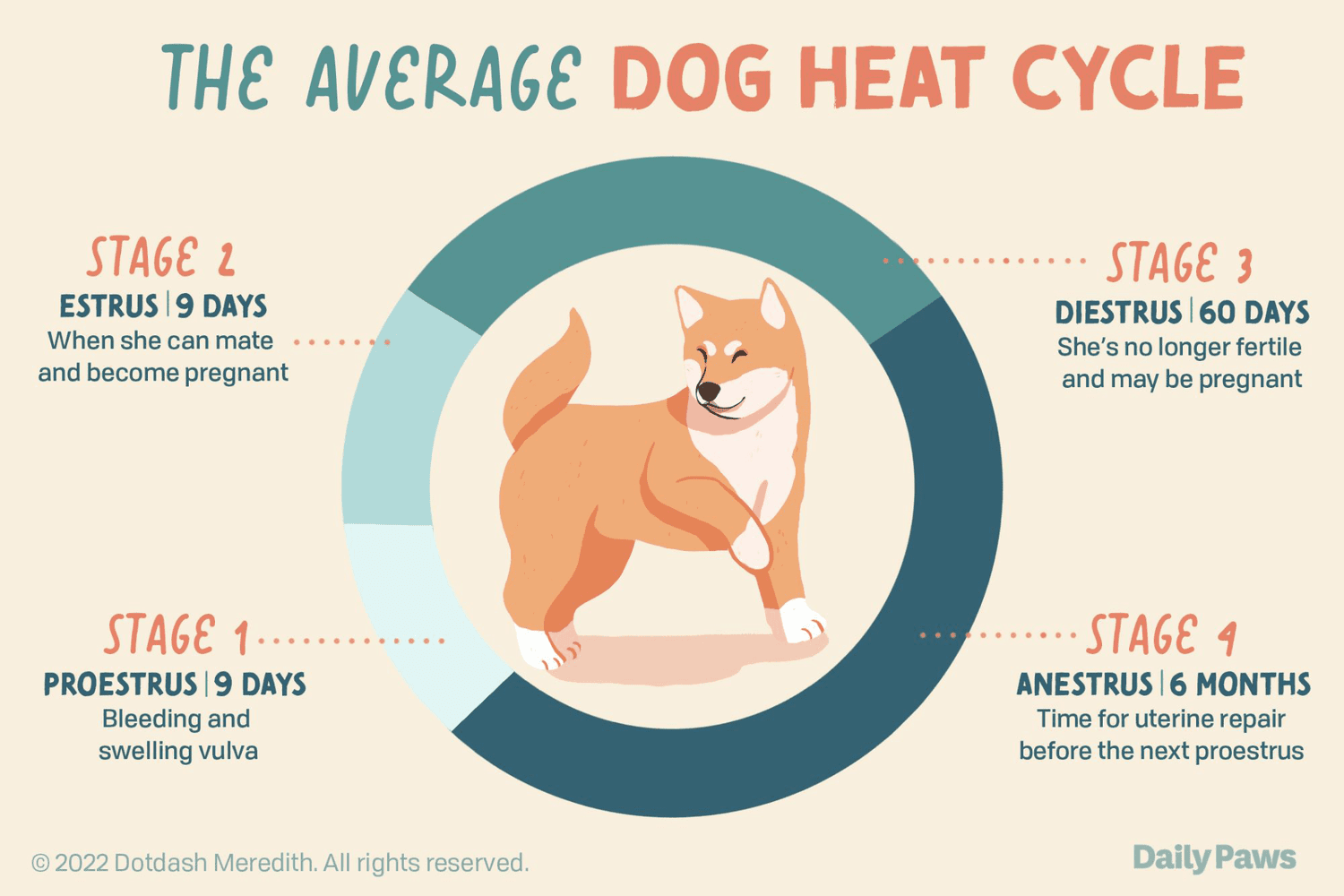
The dog reproductive cycle
Understanding the reproductive cycle of dogs is essential for dog owners, breeders, and anyone involved in the field of canine reproduction. The reproductive cycle, also known as the estrous cycle, consists of different stages that a female dog goes through. These stages are characterized by hormonal changes and physical behaviors, ultimately leading to the possibility of mating and pregnancy.
When do dogs reach sexual maturity
Dogs typically reach sexual maturity between the ages of six to twelve months, depending on the breed and individual factors. Larger breeds tend to mature later than smaller breeds. It is important to note that reaching sexual maturity does not necessarily mean the dog is mentally or emotionally ready for mating. It is recommended to wait until the dog is fully developed and matured before considering breeding.
How often do female dogs come into heat
Female dogs typically come into heat, or estrus, every six to twelve months. However, this can vary depending on the individual dog. Some dogs may have irregular heat cycles, while others may go into heat more frequently. It is essential for owners to monitor their female dogs closely during this time to prevent unwanted pregnancies and ensure their well-being.
The Mating Process in Dogs
The stages of dog mating
The mating process in dogs consists of several stages. It starts with the initial attraction and courtship behaviors, where the male dog displays interest in the female. This is followed by mounting and intromission, where the male dog penetrates the female’s reproductive tract. After successful mating, the male and female dogs may remain locked together, known as the “tie,” which allows for the transfer of sperm. Finally, the dogs separate, and the female may display certain post-mating behaviors.
How long does mating take
The duration of mating can vary from a few minutes to over an hour, depending on the dogs involved. Some dogs may engage in multiple matings over a few days to increase the chances of successful fertilization. It is important to allow the dogs to mate naturally and not to rush the process.
Behaviors to expect during and after mating
During mating, both male and female dogs may display certain behaviors. Male dogs may become more assertive and dominant, while female dogs may show signs of receptiveness and submission. After mating, the female dog may experience a temporary change in behavior, such as restlessness, decreased appetite, or nesting behaviors. These behaviors are normal and typically subside within a few days.
Bleeding After Mating
Why some dogs bleed after mating
It is not uncommon for female dogs to experience bleeding after mating. This bleeding, known as post-mating bleeding, is caused by the physical trauma to the female’s reproductive tract during mating. The male dog’s penis has a bulbous gland at the base, which causes slight tearing of the vaginal tissues. This tearing can result in mild to moderate bleeding.
Distinguishing normal from abnormal bleeding
It is important to distinguish between normal post-mating bleeding and abnormal bleeding. Normal post-mating bleeding is typically mild, lasts for a short duration, and gradually decreases over time. Abnormal bleeding, on the other hand, may be excessive, prolonged, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms. If the bleeding seems excessive or if you notice any signs of distress or discomfort in your female dog, it is crucial to seek veterinary care.
Signs of post-mating bleeding
Signs of post-mating bleeding may include spotting of blood on the bedding or floor, bloodstains on the female dog’s hindquarters, or the presence of blood in her urine. The bleeding should gradually decrease in intensity and duration. However, if the bleeding persists or becomes heavier, it may be a sign of a more serious underlying issue and should be evaluated by a veterinarian.
Normal Post-Mating Bleeding Duration
Average duration of post-mating bleeding
The average duration of post-mating bleeding in female dogs is typically around 7 to 10 days. However, this can vary depending on factors such as the individual dog, the breed, and the number of matings that occurred. It is important to note that this is just an average, and some dogs may have shorter or longer durations of bleeding.
Factors affecting the length of post-mating bleeding
Several factors can influence the length of post-mating bleeding in female dogs. These factors may include the breed of the dog, the number of matings that occurred, and the overall health of the dog. It is essential to observe and monitor the bleeding closely to ensure that it remains within a normal range.
How to monitor bleeding after mating
To monitor the bleeding after mating, regularly check the dog’s bedding and inspect her hindquarters for any signs of blood. Keep a record of the duration and intensity of the bleeding, as well as any changes in behavior or additional symptoms. If you notice any concerning changes or if the bleeding persists beyond the normal duration, it is advisable to consult with a veterinarian.

When Post-Mating Bleeding is a Problem
Complications that cause excessive or prolonged bleeding
While post-mating bleeding is generally considered normal, there are certain complications that can cause excessive or prolonged bleeding. These complications may include infections, trauma to the reproductive tract, hormonal imbalances, or underlying medical conditions. If the bleeding is severe, lasts longer than the normal duration, or is accompanied by other worrying symptoms, it is crucial to seek veterinary care.
How to identify problem bleeding
Problematic post-mating bleeding can be identified by its severity, duration, and the presence of additional symptoms. If the bleeding is heavy, continuous, or if the dog shows signs of distress such as persistent pain, lethargy, or loss of appetite, it could indicate a problem. It is important not to ignore these signs and to seek professional veterinary advice.
When to seek veterinary care
It is recommended to seek veterinary care if the post-mating bleeding is excessive, lasts longer than expected, or if the dog shows signs of discomfort or distress. Additionally, if there are any accompanying symptoms such as fever, discharge with a foul odor, or changes in behavior, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian. Timely veterinary intervention can help identify and resolve any underlying issues contributing to the abnormal bleeding.
Medical Causes of Post-Mating Bleeding
Possible illnesses or conditions causing bleeding
There are several medical conditions that can cause post-mating bleeding in female dogs. These conditions may include uterine infections (such as pyometra), tumors, hormonal imbalances, or abnormalities in the reproductive tract. It is essential to consult with a veterinarian for a thorough examination to determine the cause of the bleeding and to initiate appropriate treatment.
Infections that may cause post-mating bleeding
Infections of the reproductive tract, such as uterine infections, can lead to post-mating bleeding in dogs. These infections can be bacterial or fungal in nature and are typically associated with a weakened immune system or previous reproductive complications. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of such infections are vital to prevent further complications and ensure the dog’s well-being.
Trauma and bleeding after mating
Physical trauma to the reproductive tract during mating can result in post-mating bleeding. This trauma can be caused by forceful or rough mating, excessive thrusting, or anatomical abnormalities. It is important to ensure that mating occurs in a controlled and gentle manner to minimize the risk of trauma. Any signs of severe trauma or persistent bleeding should be brought to the attention of a veterinarian immediately.
Non-Medical Causes of Post-Mating Bleeding
Possible stress-related causes
Stress can play a role in post-mating bleeding in dogs. Extreme levels of stress during mating can cause the female dog’s body to respond abnormally, leading to increased bleeding. This can occur if the mating environment is unfamiliar, if there is excessive noise or disruption, or if the female dog is anxious or fearful. Creating a calm and comfortable environment for mating can help reduce stress levels and minimize the risk of excessive bleeding.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and overall hygiene, can also affect post-mating bleeding in dogs. Extreme temperatures and poor hygiene can increase the risk of infections, which may contribute to abnormal bleeding. Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment, as well as ensuring appropriate temperature control, can help prevent complications and promote a healthy reproductive process.
Impact of dog temperament and behavior on post-mating bleeding
The temperament and behavior of the female dog can also impact post-mating bleeding. Aggressive or anxious behavior during mating can result in excessive struggling or resistance, increasing the risk of physical trauma and subsequent bleeding. It is important to ensure that both the male and female dogs are calm, well-behaved, and comfortable during the mating process to minimize the chances of complications.
Consulting a Vet about Post-Mating Bleeding
When to contact a vet
If you have any concerns or questions about post-mating bleeding in your dog, it is recommended to contact a veterinarian. Veterinary guidance can help determine if the bleeding is within a normal range or if further evaluation is necessary. Prompt communication with a vet can help ensure the health and well-being of your dog.
What to expect during a vet visit
During a vet visit for post-mating bleeding, the veterinarian will perform a thorough physical examination of the dog. They may ask detailed questions about the bleeding, the duration, and any accompanying symptoms. Additional diagnostic tests, such as blood work, ultrasound, or cultures, may be performed to identify any underlying causes. The vet will then discuss the findings with you and provide appropriate recommendations for treatment or further investigation.
How a vet diagnoses the cause of post-mating bleeding
To diagnose the cause of post-mating bleeding, a veterinarian will consider various factors. These may include the dog’s medical history, physical examination findings, the duration and severity of the bleeding, and any accompanying symptoms. In some cases, additional diagnostic tests may be needed, such as blood work, imaging studies, or examination of vaginal swabs. Based on the findings, the vet will establish a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan tailored to the dog’s specific needs.

Treating Post-Mating Bleeding in Dogs
Commonly prescribed treatments for post-mating bleeding
The treatment for post-mating bleeding in dogs depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the bleeding. In cases of normal post-mating bleeding, no specific treatment may be required, as it typically resolves on its own. However, if the bleeding is excessive or abnormal, treatment options may include medications to address infections or hormonal imbalances, supportive care, or surgical interventions. The vet will determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the diagnostic findings.
Home care and management of post-mating bleeding
Home care and management play a vital role in supporting the recovery of a dog experiencing post-mating bleeding. Providing a clean and comfortable environment, ensuring proper nutrition and hydration, and minimizing physical activity can help promote healing and reduce the risk of further complications. It is crucial to follow the vet’s instructions regarding any medications, monitoring the bleeding, and scheduling follow-up visits.
Complications and risks of untreated post-mating bleeding
Untreated post-mating bleeding can lead to several complications and risks to the dog’s health. These may include the development of severe infections, anemia due to excessive blood loss, or the persistence of underlying conditions causing the bleeding. Timely veterinary intervention is crucial to prevent these complications and ensure the best possible outcome for the dog.
Preventing Post-Mating Bleeding
Steps to prevent post-mating bleeding
Preventing post-mating bleeding involves taking certain steps to minimize the risk of physical trauma and infections. These steps may include ensuring a calm and controlled mating environment, avoiding excessive force during mating, and monitoring the behavior and comfort of both the male and female dogs. Additionally, regular veterinary check-ups and maintaining overall health and hygiene can help reduce the chances of complications.
Importance of regular check-ups for prevention
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for preventing post-mating bleeding and maintaining the overall reproductive health of dogs. These check-ups allow for early detection of any underlying conditions or infections that may contribute to abnormal bleeding. The vet can provide guidance on breeding practices, vaccination protocols, and general care to minimize the risk of complications during the reproductive cycle.
Healthy lifestyle habits to minimize risk of post-mating bleeding
To minimize the risk of post-mating bleeding, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle for your dog. This includes providing a balanced and nutritious diet, regular exercise, and proper grooming. Keeping stress levels low and providing a comfortable and safe environment also contribute to overall reproductive health. By adopting these healthy habits, you can help promote the well-being of your dog and reduce the likelihood of complications during the mating process.
In conclusion, understanding canine reproduction and the potential issues surrounding post-mating bleeding is essential for dog owners and breeders. By being knowledgeable about the normal behaviors and durations of post-mating bleeding, as well as recognizing signs of abnormal bleeding, dog owners can provide appropriate care and seek veterinary assistance when necessary. Timely intervention and proper management can help ensure the overall health and well-being of dogs during the reproductive cycle.

About the author
Latest Posts

How to Clean Dog Bed Pee: Expert Tips for Freshness
Master the art of cleaning dog bed pee with expert tips and tricks to ensure a fresh and odor-free environment for your furry friend.

How to Clean Dog Bedding With Vinegar: Ultimate Guide
Master the art of using vinegar to clean your dog's bedding and say goodbye to lingering odors – your furry friend deserves a fresh and cozy sleeping space!

How to Walk Dog With Stroller: Tips for Smooth Strolls
Juggle the delicate balance of walking your dog with a stroller – find out how to make this harmonious dance a breeze!

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.